atan2, atan2f, atan2l
| Definiert in Header <math.h> |
||
| float atan2f( float y, float x ); |
(1) | (seit C99) |
| double atan2( double y, double x ); |
(2) | |
| long double atan2l( long double y, long double x ); |
(3) | (seit C99) |
| _Decimal32 atan2d32( _Decimal32 y, _Decimal32 x ); |
(4) | (seit C23) |
| _Decimal64 atan2d64( _Decimal64 y, _Decimal64 x ); |
(5) | (seit C23) |
| _Decimal128 atan2d128( _Decimal128 y, _Decimal128 x ); |
(6) | (seit C23) |
| Definiert in Header <tgmath.h> |
||
| #define atan2( y, x ) |
(7) | (seit C99) |
atan2l) aufgerufen. Andernfalls, wenn ein Argument einen ganzzahligen Typ oder den Typ double hat, wird (2) (atan2) aufgerufen. Andernfalls wird (1) (atan2f) aufgerufen.|
Die Funktionen (4-6) werden nur dann deklariert, wenn die Implementierung |
(seit C23) |
Inhalt |
[edit] Parameter
| x, y | - | Gleitkommawert |
[edit] Rückgabewert
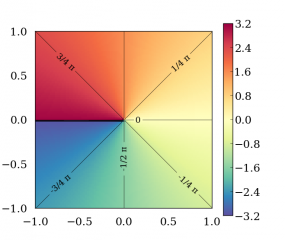
Wenn keine Fehler auftreten, wird der Arkustangens von y / x (arctan(| y |
| x |
Wenn ein Domänenfehler auftritt, wird ein implementierungsdefinierter Wert zurückgegeben.
Wenn ein Bereichsfehler aufgrund eines Unterlaufs auftritt, wird das korrekte Ergebnis (nach Rundung) zurückgegeben.
[edit] Fehlerbehandlung
Fehler werden wie in math_errhandling angegeben gemeldet.
Ein Domänenfehler kann auftreten, wenn x und y beide Null sind.
Wenn die Implementierung IEEE-Gleitkomma-Arithmetik (IEC 60559) unterstützt
- Wenn x und y beide Null sind, tritt kein Domänenfehler auf;
- Wenn x und y beide Null sind, tritt auch kein Bereichsfehler auf;
- Wenn y Null ist, tritt kein Polfehler auf;
- Wenn y
±0ist und x negativ oder-0ist, wird±πzurückgegeben; - Wenn y
±0ist und x positiv oder+0ist, wird±0zurückgegeben; - Wenn y
±∞ist und x endlich ist, wird±π/2zurückgegeben; - Wenn y
±∞ist und x-∞ist, wird±3π/4zurückgegeben; - Wenn y
±∞ist und x+∞ist, wird±π/4zurückgegeben; - Wenn x
±0ist und y negativ ist, wird-π/2zurückgegeben; - Wenn x
±0ist und y positiv ist, wird+π/2zurückgegeben; - Wenn x
-∞ist und y endlich und positiv ist, wird+πzurückgegeben; - Wenn x
-∞ist und y endlich und negativ ist, wird-πzurückgegeben; - Wenn x
+∞ist und y endlich und positiv ist, wird+0zurückgegeben; - Wenn x
+∞ist und y endlich und negativ ist, wird-0zurückgegeben; - Wenn entweder x NaN ist oder y NaN ist, wird NaN zurückgegeben.
[edit] Hinweise
atan2(y, x) ist äquivalent zu carg(x + I*y).
POSIX spezifiziert, dass im Falle eines Underflows y / x der zurückgegebene Wert ist, und wenn dies nicht unterstützt wird, ein implementierungsabhängiger Wert zurückgegeben wird, der nicht größer ist als DBL_MIN, FLT_MIN und LDBL_MIN.
[edit] Beispiel
#include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { // normal usage: the signs of the two arguments determine the quadrant // atan2(1,1) = +pi/4, Quad I printf("(+1,+1) cartesian is (%f,%f) polar\n", hypot( 1, 1), atan2( 1, 1)); // atan2(1, -1) = +3pi/4, Quad II printf("(+1,-1) cartesian is (%f,%f) polar\n", hypot( 1,-1), atan2( 1,-1)); // atan2(-1,-1) = -3pi/4, Quad III printf("(-1,-1) cartesian is (%f,%f) polar\n", hypot(-1,-1), atan2(-1,-1)); // atan2(-1,-1) = -pi/4, Quad IV printf("(-1,+1) cartesian is (%f,%f) polar\n", hypot(-1, 1), atan2(-1, 1)); // special values printf("atan2(0, 0) = %f atan2(0, -0)=%f\n", atan2(0,0), atan2(0,-0.0)); printf("atan2(7, 0) = %f atan2(7, -0)=%f\n", atan2(7,0), atan2(7,-0.0)); }
Ausgabe
(+1,+1) cartesian is (1.414214,0.785398) polar (+1,-1) cartesian is (1.414214,2.356194) polar (-1,-1) cartesian is (1.414214,-2.356194) polar (-1,+1) cartesian is (1.414214,-0.785398) polar atan2(0, 0) = 0.000000 atan2(0, -0)=3.141593 atan2(7, 0) = 1.570796 atan2(7, -0)=1.570796
[edit] Referenzen
- C23-Standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2024)
- 7.12.4.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. TBD)
- 7.25 Typ-generische Mathematik <tgmath.h> (S. TBD)
- F.10.1.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. TBD)
- C17-Standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2018)
- 7.12.4.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. 174)
- 7.25 Typ-generische Mathematik <tgmath.h> (S. 272-273)
- F.10.1.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. 378)
- C11-Standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2011)
- 7.12.4.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. 239)
- 7.25 Typ-generische Mathematik <tgmath.h> (S. 373-375)
- F.10.1.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. 519)
- C99-Standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1999)
- 7.12.4.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. 219)
- 7.22 Typ-generische Mathematik <tgmath.h> (S. 335-337)
- F.9.1.4 Die atan2-Funktionen (S. 456)
- C89/C90-Standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1990)
- 4.5.2.4 Die atan2-Funktion
[edit] Siehe auch
| (C99)(C99) |
berechnet Arkussinus (arcsin(x)) (Funktion) |
| (C99)(C99) |
berechnet Arkuskosinus (arccos(x)) (Funktion) |
| (C99)(C99) |
berechnet Arkustangens (arctan(x)) (Funktion) |
| (C99)(C99)(C99) |
berechnet den Phasenwinkel einer komplexen Zahl (Funktion) |
| C++-Dokumentation für atan2
| |